Implementation Science and Research
Category: Implementation Science and Research
Poster Theater Session VI
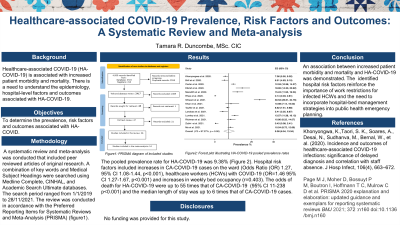
ISR 81 - Healthcare-associated COVID-19 Prevalence, Risk Factors and Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Wednesday, June 5, 2024
9:47 AM - 9:52 AM CST
Location: Digital Poster Theater - APIC Central, Hall 1
Has Audio

Tamara Duncombe, MSc, CIC
Epidemiologist
Fraser Health Authority
Presenter(s)
Disclosure(s):
Tamara Duncombe, MSc, CIC: No financial relationships to disclose
Background: Compared to Community-acquired COVID-19 (CA-COVID-19), healthcare-associated COVID-19 (HA-COVID-19) is associated with increased patient morbidity and mortality. There is a need to understand the epidemiology, the associated outcomes and hospital-level risk factors associated with HA-COVID-19 in acute care settings.
Methods: This systematic review included peer-reviewed articles reporting one or more related to HA-COVID-19: i) prevalence or incidence, ii) risk factors and iii) outcomes. Articles were limited to those of the English language and adults admitted to acute care settings between January 1, 2020, and November 28, 2021. A random-effects meta-analysis was conducted to estimate the prevalence of HA-COVID-19. Risk factors and outcomes were summarized.
Results: Included were 26 studies, of which 65% were conducted in the United Kingdom. The meta-analysis included 14 studies involving 9369 COVID positive cases. The pooled prevalence rate for HA-COVID-19 was 9.38% (95% Confidence Interval [CI]: 6.06% -13.34%; Q= 476.29; I2 97.27%; p< 0.001). Twelve studies reported risk factors associated with HA-COVID-19, two of which reported on hospital and patient-level risk factors. Increases in HA-COVID-19 were associated with increases in CA-COVID-19 cases on the ward, Odds Ratio (OR) 1.27, 95% CI 1.08-1.44, p< 0.001, healthcare workers (HCW) with COVID-19 (OR=1.46 95% CI 1.27 to 1.67, p< 0.001) and increases in weekly bed occupancy (r=0.403). The odds of death for HA-COVID-19 were up to 55 times that of CA-COVID-19 (95% CI 11-238 p< 0.001), and the median length of stay was up to 6 times that of CA-COVID-19 cases.
Conclusions: Approximately 10% of COVID-19 cases were healthcare-associated and were associated with increased patient morbidity and mortality. Sick HCW and increased bed occupancy were positively associated with HA-COVID-19. These findings reinforce the importance of work restrictions for infected HCWs and the need to incorporate hospital-bed management strategies into public health emergency planning and during the management of such threats.
Learning Objectives:
- Upon completion, participants will be able to describe the prevalence of healthcare-associated COVID-19.
- Upon completion, participants will be able to describe the risk factors associated with healthcare-associated COVID-19 transmission.
- Upon completion, participants will be able to describe the outcomes associated with healthcare-associated COVID-19.

